Language structure
These are the basic units of the language, from the simplest to the most complex:
1. Phoneme: /d/ /k/ /l/
a phoneme es a distinctive speech sound. Phonemes are represented by phonetic transcription.
2. The syllable: en inglés al igual que espeñol las sílabas son conjuntos de sonidos. Ejem: casa- /ka/ /sa/ dos sílabas mice /mais/ una silaba.
A syllable es made up of one or more phonemes.
3. the word: daughter, cat, mouse...
A word is considered the smallest unit of the languaje capable of carrying a meaning. It can be made up of one or more syllables.
4. The phrase: an old sport cars, In the park...
A phrase in made uo of two or more words which together make up a particular element -the subject or the object - of the clause. Phrases can be classified into:
*Noun phrases (they function as subject or object)
*Verb phrases
*Adverb phrases
5. The clause: The old man was on television (main clause), The old man
whose son died in the accident(subordinate clause).
A clause is a group of words which contains a subject and a finite verb, and it may also contain an object or an adverb. The three types of clauses are:
*Main clause: it provides a complete expression of meaning and can stand independently.
*Subordinate clause: it cannot stand independently and is dependent on a main clause. It is
usually introduced by a conjunction.
*Coordinate clause: it is one of two clauses which could each stand as independent sentence and are
joined together, ususally linkend by and, but or or.
6. The sentence: The old man whose son died in the accident was on television.
A sentence provides a complete expression of meaning. It is made up of one or more clauses. It can express a statement, a question, a command or an exclamation. If the sentence is an imperative, it may not have a subject. In case of an exclamation it may not have a verb.
Homework:
* Copiar en la libreta y traducir.
* Buscar 5 ejemplos de cada uno de los seis puntos.
* Read these sentences and identify phonemes, syllables, words, phrases and clauses. (y poner de qué tipos son casa una).
-We bought the sofa because it was cheap.
- As we drove past the park, we saw some people lying on the grass.
- Whrn he fell over, he broke two of his teeth.
- We've got some flour, but we haven't got any sugar.
- We packed our suitcases and left in a hurry.
* Make your own sentences and mark the phonemes, syllables, words, phrases and clauses. (y poner de qué tipos son casa una).
*
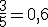 )
) 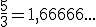 )
) 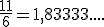 ).
).
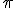 =3,1415926...... o
=3,1415926...... o 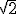 =1,41421356... Estos números se llaman irracionales.
=1,41421356... Estos números se llaman irracionales.
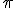 =3,1415926...... o
=3,1415926...... o 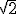 =1,41421356... Estos números se llaman irracionales.
=1,41421356... Estos números se llaman irracionales.
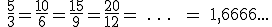
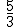 .
.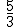 .
.
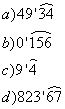
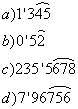








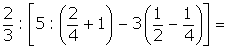







- Follow Us on Twitter!
- "Join Us on Facebook!
- RSS
Contact